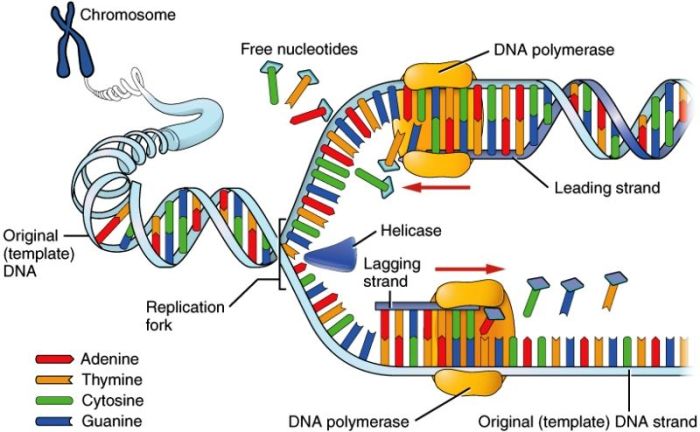
Match these enzymes involved in DNA replication with their function, an intriguing topic that unveils the intricate mechanisms underlying the perpetuation of genetic material. DNA polymerase, RNA primase, helicase, DNA ligase, and topoisomerase play pivotal roles in this fundamental process, ensuring the accurate duplication of genetic information.
As we delve into the functions of these enzymes, we will uncover their significance in maintaining genetic stability, initiating DNA synthesis, unwinding the DNA double helix, joining DNA fragments, and preventing DNA tangles. Their coordinated actions orchestrate the precise replication of DNA, the blueprint of life, essential for cell division and the inheritance of genetic traits.
DNA Replication Enzymes
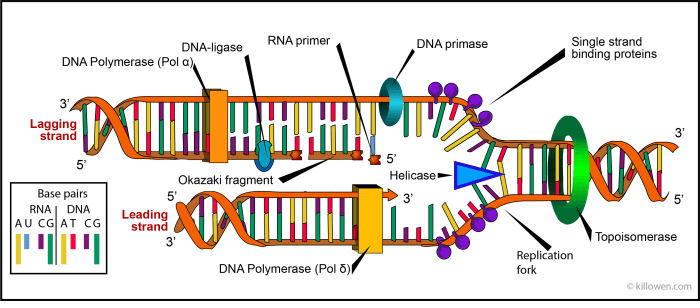
DNA replication is a complex and essential process for all living organisms. It ensures the accurate duplication of genetic material during cell division. Several key enzymes play crucial roles in this process, each with a specific function.
DNA Polymerase, Match these enzymes involved in dna replication with their function
DNA polymerase is the primary enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands during replication. It catalyzes the addition of nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, ensuring that the newly synthesized strand is complementary to the template strand.
There are different types of DNA polymerases, each with specific roles:
- DNA polymerase I: Involved in repairing damaged DNA and synthesizing short DNA fragments during replication.
- DNA polymerase III: The main enzyme responsible for DNA synthesis during replication, highly processive and efficient.
- DNA polymerase IV: Specialized in synthesizing across DNA lesions or damaged regions.
DNA polymerase is essential for maintaining genetic stability by ensuring the accuracy of DNA replication.
RNA Primase
RNA primase is an enzyme that synthesizes short RNA primers, which are essential for initiating DNA synthesis.
During replication, RNA primase binds to the template strand and synthesizes a short RNA primer complementary to the template. This primer provides a starting point for DNA polymerase to add nucleotides and extend the DNA strand.
RNA primers are later removed by DNA polymerase I, which replaces them with DNA nucleotides.
Helicase
Helicase is an enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix, making the template strands accessible for replication.
Helicase binds to the DNA double helix and moves along the strands, breaking the hydrogen bonds between base pairs and separating the two strands.
Helicase is essential for initiating DNA replication and allowing other replication enzymes to access the template strands.
DNA Ligase
DNA ligase is an enzyme that joins the newly synthesized DNA fragments together, completing the DNA replication process.
During replication, DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA fragments called Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. DNA ligase joins these fragments together by catalyzing the formation of phosphodiester bonds between the adjacent nucleotides.
DNA ligase is essential for completing DNA replication and ensuring the integrity of the newly synthesized DNA strand.
Topoisomerase
Topoisomerase is an enzyme that prevents DNA tangles and supercoiling during replication.
During replication, the DNA double helix can become twisted or supercoiled due to the unwinding action of helicase.
Topoisomerase relaxes the supercoils by breaking and rejoining the DNA backbone, allowing the DNA double helix to remain accessible for replication.
Top FAQs: Match These Enzymes Involved In Dna Replication With Their Function
What is the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
DNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands during DNA replication. It adds nucleotides to the growing DNA strand, following the template strand.
How does RNA primase initiate DNA synthesis?
RNA primase synthesizes short RNA primers that provide a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin DNA synthesis.
What is the function of helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, separating the two strands to make the template strand accessible for DNA polymerase.
How does DNA ligase complete the DNA replication process?
DNA ligase joins the fragments of newly synthesized DNA, creating a continuous DNA strand.
What is the importance of topoisomerase in DNA replication?
Topoisomerase prevents DNA tangles by relaxing the supercoiled DNA molecule, allowing DNA polymerase and other enzymes to access the DNA template.