Introducing the Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key, your ultimate guide to mastering the intricacies of geometry. This comprehensive resource provides a thorough overview of fundamental concepts, problem-solving techniques, theorems, and their applications in real-world scenarios.
Embark on an engaging journey as we delve into the depths of geometry, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to tackle any geometry challenge with confidence.
Geometry Chapter 8 Review
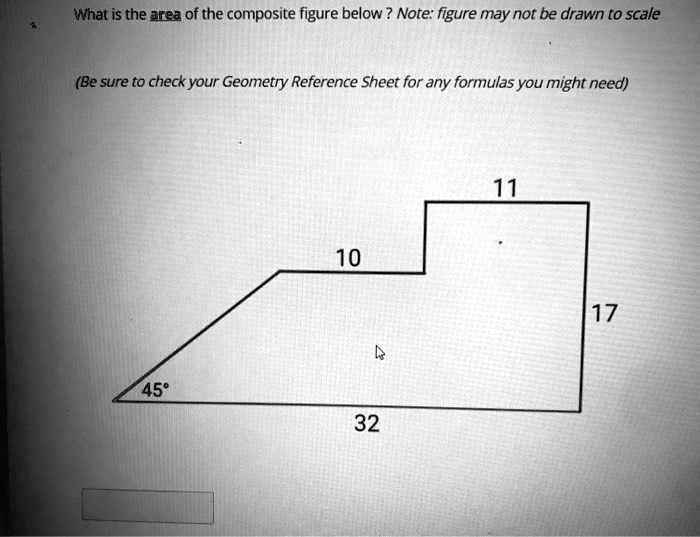
Geometry Chapter 8 covers the fundamentals of geometry, including concepts, problem-solving techniques, theorems, and their applications in real-world scenarios. This review will provide a comprehensive overview of the chapter’s key elements.
Concepts and Definitions
Geometry Chapter 8 introduces several fundamental concepts:
- Points, Lines, and Planes:Points represent locations in space, lines extend infinitely in one direction, and planes are flat surfaces that extend indefinitely.
- Angles:Angles are formed by two rays or line segments that share a common endpoint, measured in degrees.
- Triangles:Triangles are polygons with three sides and three angles.
- Circles:Circles are closed, plane figures defined by a set of points equidistant from a fixed point called the center.
Problem-Solving Techniques
Chapter 8 presents various problem-solving strategies:
- Drawing Diagrams:Creating visual representations of geometric figures helps visualize relationships and identify patterns.
- Using Properties and Theorems:Applying known properties and theorems to simplify problems and deduce unknown information.
- Solving Equations:Setting up and solving equations involving geometric variables, such as angles and lengths.
- Proof by Contradiction:Assuming the opposite of a statement to derive a contradiction and prove the original statement.
Theorems and Proof
Chapter 8 introduces several key theorems:
- Pythagorean Theorem:Relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle.
- Angle Bisector Theorem:Divides an angle into two congruent angles and intersects the opposite side of the triangle in a segment that bisects the side.
- Triangle Inequality Theorem:The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side.
Applications in Real-World Situations
Geometry Chapter 8 concepts find applications in various fields:
- Architecture:Designing buildings and structures using geometric principles.
- Engineering:Analyzing forces and stresses in structures.
- Navigation:Calculating distances and angles for travel.
- Art and Design:Creating visual compositions using geometric shapes and patterns.
Review Questions and Answers, Geometry chapter 8 review answer key
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 cm and a height of 8 cm. | 40 cm2 |
| Prove that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. | Use the Angle Sum Theorem and the fact that the sum of the angles around a point is 360 degrees. |
Additional Resources
FAQ Resource: Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key
What is the purpose of the Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key?
The Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key is designed to provide students with a comprehensive review of the concepts and problem-solving techniques covered in Geometry Chapter 8, ensuring a deep understanding of the subject matter.
How can I use the Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key effectively?
To effectively utilize the Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key, engage with the content actively, reviewing the concepts and problem-solving techniques presented. Practice solving problems using the strategies Artikeld in the key to reinforce your understanding.
What are the benefits of using the Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key?
The Geometry Chapter 8 Review Answer Key offers numerous benefits, including improved comprehension of geometry concepts, enhanced problem-solving skills, increased confidence in tackling geometry challenges, and a solid foundation for further geometry studies.