As “Which of the Following Statements Regarding Gonorrhea is Correct?” takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with academic precision and authoritative tone, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. With a comprehensive examination of transmission, diagnosis, prevention, and global impact, this discourse delves into the complexities of gonorrhea, shedding light on its prevalence, complications, and the strategies employed to combat its spread.
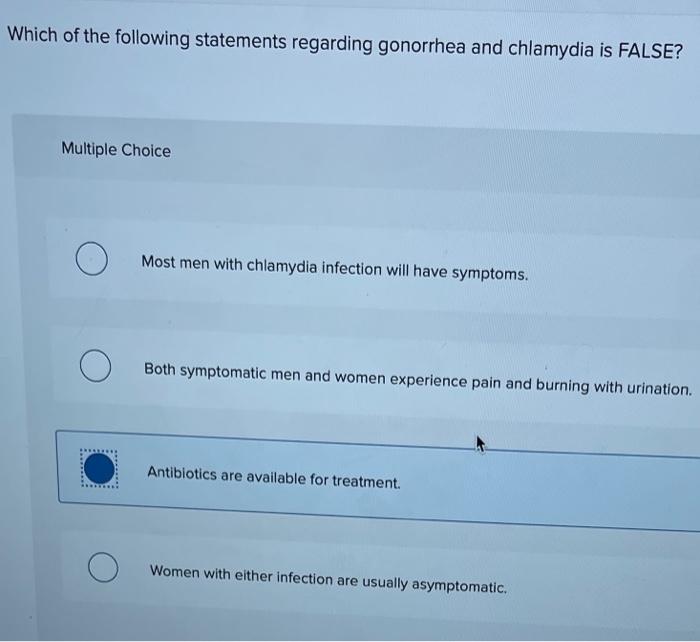
The discourse unfolds with a detailed exploration of gonorrhea’s transmission dynamics and the common symptoms associated with the infection. It delves into the potential complications and long-term effects of untreated gonorrhea, emphasizing the importance of prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The discussion then shifts to the various methods used to diagnose gonorrhea, including laboratory tests and physical examinations, highlighting the significance of accurate and timely diagnosis for effective management.
Gonorrhea Transmission and Symptoms
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Individuals infected with gonorrhea may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Painful or burning sensation during urination
- Increased frequency of urination
- Unusual discharge from the vagina or penis
- Pelvic pain in women
- Swelling or pain in the testicles in men
If left untreated, gonorrhea can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women
- Epididymitis (inflammation of the epididymis) in men
- Infertility
- Increased risk of HIV infection
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gonorrhea: Which Of The Following Statements Regarding Gonorrhea Is Correct
Gonorrhea is diagnosed through laboratory tests, which may include:
- Gram staining
- Culture
- Nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs)
Treatment for gonorrhea typically involves antibiotics, such as:
- Ceftriaxone
- Azithromycin
- Doxycycline
It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Prevention and Control of Gonorrhea
Effective strategies for preventing gonorrhea transmission include:
- Consistent condom use during all sexual activity
- Limiting the number of sexual partners
- Avoiding unprotected sex with individuals who have symptoms of an STI
Public health measures also play a crucial role in controlling gonorrhea:
- Contact tracing and partner notification
- Education and awareness campaigns
- Regular STD screenings and testing
Epidemiology and Global Impact of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a major public health concern, with an estimated 87 million new cases worldwide each year.
- It is more prevalent in certain populations, such as young people, men who have sex with men (MSM), and individuals living in low- and middle-income countries.
- Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and lack of access to healthcare, contribute to the spread of gonorrhea.
- Controlling and eliminating gonorrhea requires a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and public health measures.
FAQ Guide
What are the common symptoms of gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea often presents with symptoms such as burning sensation during urination, increased urinary frequency, unusual discharge from the genitals, and pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen.
How is gonorrhea diagnosed?
Gonorrhea is typically diagnosed through laboratory tests, such as urine tests or swabs from the infected area, which are analyzed to detect the presence of the bacteria responsible for the infection.
What are the potential complications of untreated gonorrhea?
Untreated gonorrhea can lead to severe complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease in women, infertility in both men and women, and an increased risk of acquiring and transmitting HIV.
How can gonorrhea be prevented?
Gonorrhea can be prevented by practicing safe sex, using condoms consistently and correctly, and undergoing regular STD screenings for early detection and treatment.