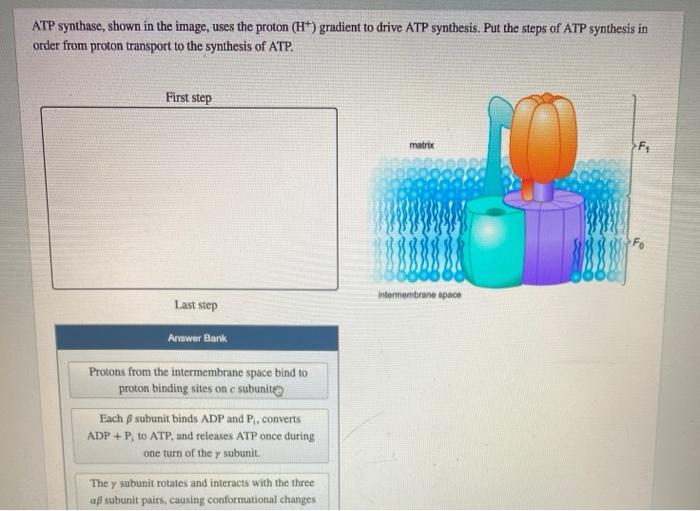
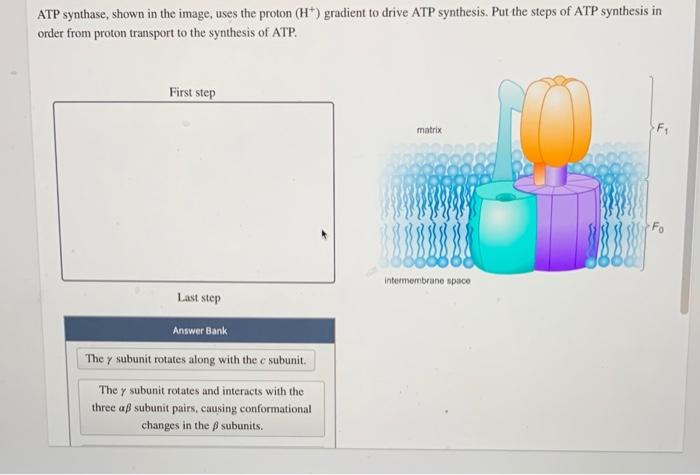
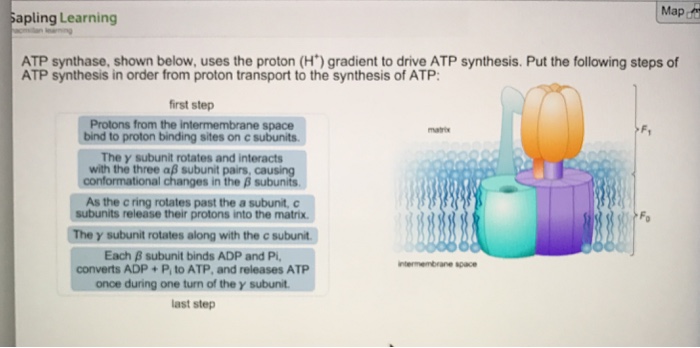
Atp synthase shown in the image uses the proton – ATP synthase, a molecular marvel found within the mitochondrial membrane, plays a pivotal role in cellular energy production by harnessing the proton gradient across the membrane. This remarkable enzyme exemplifies the intricate interplay between biochemistry and bioenergetics, orchestrating the synthesis of ATP, the universal energy currency of life.
ATP synthase’s intricate structure and mechanism, driven by proton flow, are explored in this comprehensive overview. We delve into its regulation, compare it to other ATP-synthesizing enzymes, and uncover its clinical significance in cellular energy metabolism.
ATP Synthase
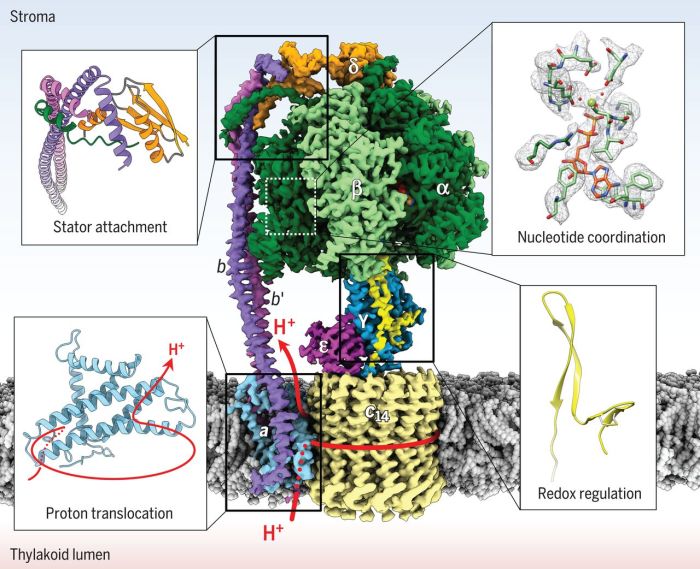
ATP synthase adalah enzim yang mengkatalisis sintesis adenosin trifosfat (ATP), mata uang energi seluler, menggunakan gradien elektrokimia proton.Gradien elektrokimia proton, juga dikenal sebagai Proton Motive Force (PMF), dihasilkan oleh rantai transpor elektron dan merupakan sumber energi untuk sintesis ATP.
Proton Motive Force (PMF)
PMF adalah gaya pendorong yang mendorong proton melintasi membran biologis, menciptakan gradien konsentrasi dan muatan listrik.Dalam mitokondria, PMF dihasilkan oleh rantai transpor elektron, yang memompa proton dari matriks mitokondria ke ruang antar membran, menciptakan perbedaan konsentrasi proton. Perbedaan konsentrasi ini menghasilkan gradien elektrokimia yang mendorong proton kembali ke matriks melalui ATP synthase.
Struktur dan Fungsi ATP Synthase
ATP synthase adalah kompleks protein besar yang tertanam di membran biologis. Ini terdiri dari dua domain utama:
-
-*Domain F0
Sebuah kanal proton yang memungkinkan proton mengalir melintasi membran.
-*Domain F1
Sebuah bola kepala yang berisi situs aktif untuk sintesis ATP.
Domain F0 berisi c-ring, cincin protein yang berputar saat proton mengalir melaluinya. Rotasi c-ring mendorong perubahan konformasi pada domain F1, yang mengkatalisis sintesis ATP.
Regulasi ATP Synthase
Aktivitas ATP synthase diatur oleh beberapa faktor, termasuk:
Gradien pH
Gradien pH yang tinggi meningkatkan laju sintesis ATP.
Ketersediaan substrat
Ketersediaan ADP dan fosfat mempengaruhi laju sintesis ATP.
Inhibitor
Inhibitor seperti oligomycin menghambat sintesis ATP dengan memblokir aliran proton melalui domain F0.
Perbandingan dengan Enzim Sintesis ATP Lainnya, Atp synthase shown in the image uses the proton
ATP synthase adalah salah satu dari beberapa enzim yang dapat mensintesis ATP. Enzim lain termasuk:
-
-*F-type ATPases
Mirip dengan ATP synthase, tetapi menggunakan gradien ion natrium atau kalium sebagai sumber energi.
-*V-type ATPases
Menggunakan gradien pH sebagai sumber energi dan ditemukan dalam vesikel intraseluler.
Signifikansi Klinis
Disfungsi ATP synthase dapat menyebabkan berbagai penyakit, termasuk:
Sindrom Leigh
Penyakit mitokondria yang disebabkan oleh mutasi pada gen yang mengkode protein ATP synthase.
Miopati mitokondria
Penyakit otot yang disebabkan oleh mutasi pada gen yang mengkode protein ATP synthase.
Essential FAQs: Atp Synthase Shown In The Image Uses The Proton
What is the primary function of ATP synthase?
ATP synthase’s primary function is to synthesize ATP, the cellular energy currency, by harnessing the proton gradient across the mitochondrial membrane.
How is the proton gradient generated?
The proton gradient is generated by the electron transport chain, which pumps protons across the mitochondrial membrane, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
What is the role of the c-ring in ATP synthase?
The c-ring is a component of ATP synthase that rotates as protons flow through it, driving the conformational changes necessary for ATP synthesis.
How is ATP synthase regulated?
ATP synthase is regulated by various factors, including the pH gradient, substrate availability, and inhibitors, ensuring that ATP production is matched to cellular energy demands.
What is the clinical significance of ATP synthase dysfunction?
ATP synthase dysfunction can lead to cellular energy depletion and is associated with various diseases, including mitochondrial disorders and neurodegenerative diseases.